| S.N | Hormones | Enzymes |
| 1. | These are secreted by endocrine glands. | These are secreted by exocrine glands. |
| 2. | They are poured directly into the blood stream. | They are released through the ducts. |
| 3. | They have low molecular weight. | They have high molecular weight. |
| 4. | They can diffuse through the cell membrane. | They cannot diffuse through the cell membrane. |
| 5. | May act on the different site other than where they are produced. | May act at the site of their origin or may pass to their site of action through ducts. |
| 6. | Hormone regulated processes are not reversible. | Enzymes regulated processes are reversible. |
| 7. | Known as the chemical messenger of the body. | They don’t carry the messages. |
| 8. | They may be aminoacids derivatives, peptides, proteins or steroids in nature. | They are always proteinaceous in nature. |
| 9. | Produced in less quantity. | Produced in more quantity. |
| 10. | Involved in metabolic activities. | Involved in digestion. |
| 11. | Reaction is slow. | Reaction is fast. |
| 12. | Tend to change with age. | Do not change with age. |
| 13. | Excess or reduced levels cause diseases. | Insufficiency causes diseases |
| 14. | They are not known as catalyst. | They are known as biological catalyst. |
| 15. | Have diverse functions in controlling growth, development, and reproduction. | Have unique or essential functions in the body. |
| 16. | Not affected by temperature and pH. | Affected by temperature and pH. |
| 17. | Controlled by feedback (secretion or production) mechanism. | Controlled by hormone, physical or chemical effects. |
| 18. | e.g: growth hormone, ACTH, prolactin, parathormone, androgen, etc. | e.g: lipase, catalase, hydrolase, amylase, etc. |
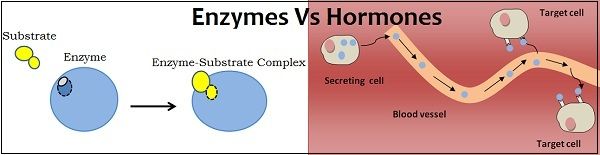
Image source: biodifference
Reference:
i) https://pediaa.com/difference-between-hormone-and-enzyme/
ii) https://biologysir.com/what-is-the-difference-between-hormones-and-enzymes/

