| S.N | Algae | Fungi | |
| 1. | They belong to kingdom Monera and Plantae. | They belong to kingdom fungi. | |
| 2. | Mode of nutrition is autotrophic. | Mode of nutrition is saprophytic or parasitic. | |
| 3. | They are photosynthetic. | They are non- photosynthetic. | |
| 4. | They contain chlorophyll. | They do not contain chlorophyll. | |
| 5. | They may be unicellular or multicellular. | They are all multicellular except yeast. | |
| 6. | Cell wall is made up of cellulose. | Cell wall is made up of chitin and cellulose. | |
| 7. | Reserve form of the food is starch. | Reserve form of the food is glycogen. | |
| 8. | Body is filamentous or parenchymatous. | Body is filamentous or pseudo parenchymatous. | |
| 9. | Incapable of living in the dark. | Capable of living in the dark. | |
| 10. | Cyanobacteria are prokaryotes, others are eukaryotes. | They are eukaryotes. | |
| 11. | Mostly aquatic– found in fresh and marine water. | They are almost terrestrial in nature. | |
| 12. | Its study is called phycology. | Its study is called mycology. | |
| 13. | Usually green in colour. | Never green and are colourless and sometimes bright coloured. | |
| 14. | They have less parasitic activity. | They have more parasitic activity. | |
| 15. | Sexual reproduction shows progressive complexity. | Sexual reproduction shows progressive simplicity. | |
| 16. | There is no dikaryotic phase. | There is distinct dikaryotic phase in some fungi. | |
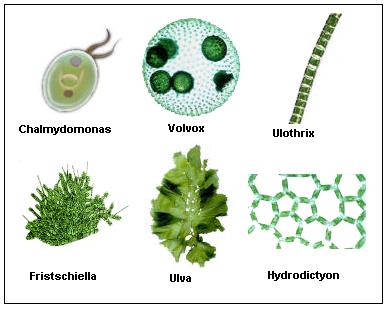
| 17. | Examples: Spirogyra, Diatoms, Oscillatoria, etc.
Image source: agrihunt |
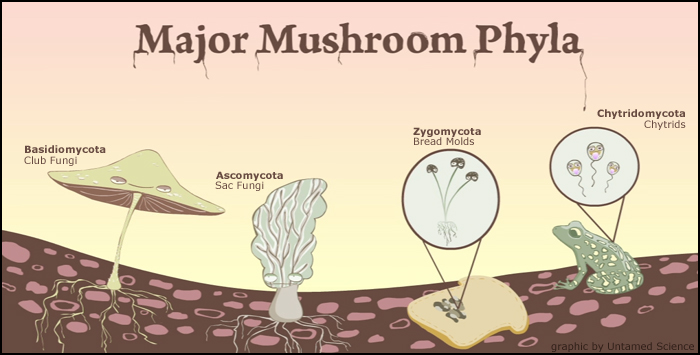
Examples: Mushroom, Candida spp., Aspergillus spp, etc.
Image source: untamed |
|
References:
i) https://unacademy.com/content/neet-ug/difference-between/algae-and-fungi/