| Chlorophyceae | Phaeophyceae | Rhodophyceae |
| Commonly known as green algae. | Commonly known as brown algae. | Commonly known as red algae. |
| Mostly found in aquatic habitats. | Mostly marine. | Mostly found in warm marine water. |
| A few are terrestrial or marine. | Only a few are found in fresh water. | A few are found in fresh water. |
| Chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b, carotenes and xanthophyll are photosynthetic pigments. | Brown coloured pigments like carotenoids, fucoxanthins, chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-c are present. | Phycoerythrin, phycocyanin, chlorophyll-a,d, carotene and xanthophyll are pigments. |
| Reproduce by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods. | Reproduce by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods. | Reproduce by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods. |
| Unicellular and multicellular. | Unicellular forms are absent. | Mostly multicellular. |
| Starch is the form of stored food. | Laminarian starch and manitol are stored food forms. | Floridean starch is the stored food form. |
| Inner layer of cell wall is made of cellulose and the outer layer is made of pectose. | Outer alginic layer and inner cellulosic. | Outer layer is pectic and inner layer is cellulosic. |
| Asexual reproduction by aplanospore or zoospore formation. | Asexual reproduction by zoospore formation. | Asexual reproduction by several types of non motiles spore formation. |
| Sexual reproduction by isogamous, anisogamous and oogamous type. | Isogamous, anisogamous and oogamous type. | Oogamous type of sexual reproduction. |
| Example: Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Ulva, etc. | Example: Fucus, Laminaria, Sargassum, etc. | Example: Batracospermum, Polysiphonia, etc. |
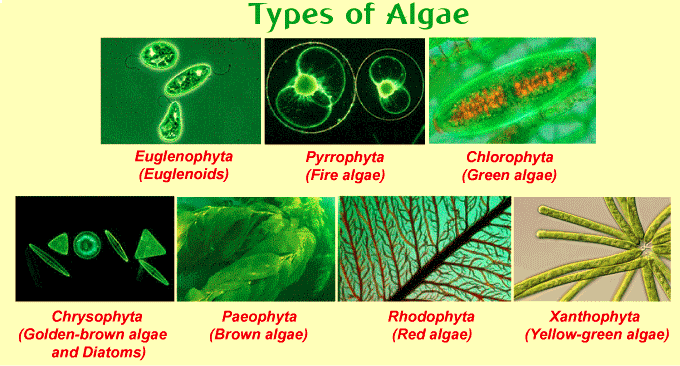
Image source: javatpoint
References:
i) https://www.thoughtco.com/types-of-marine-algae-2291975

