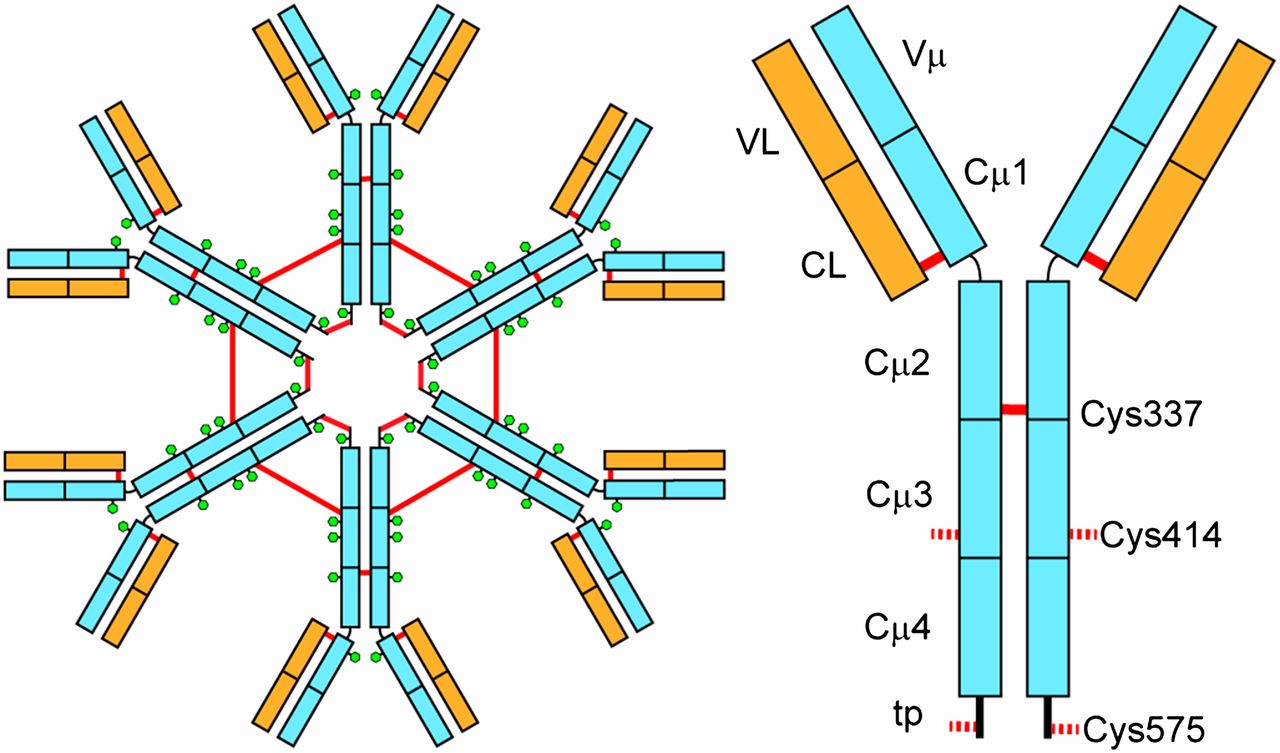
Mycoplasma: Introduction, Morphology and Biochemical Reactions
Introduction Smallest micro organisms Free living in nature Can grow in cell free medium Causes human infection M. pneumoniae: Pneumonia Ureaplasma urealyticum: non-gonococcal urethritis M. hominis and M. gentalium: genital tract infections. Cell wall absent Highly pleomorphic in nature Has no fixed shape and size Absence of cell wall precursors that are Muramic acid diaminopimelic … Read more