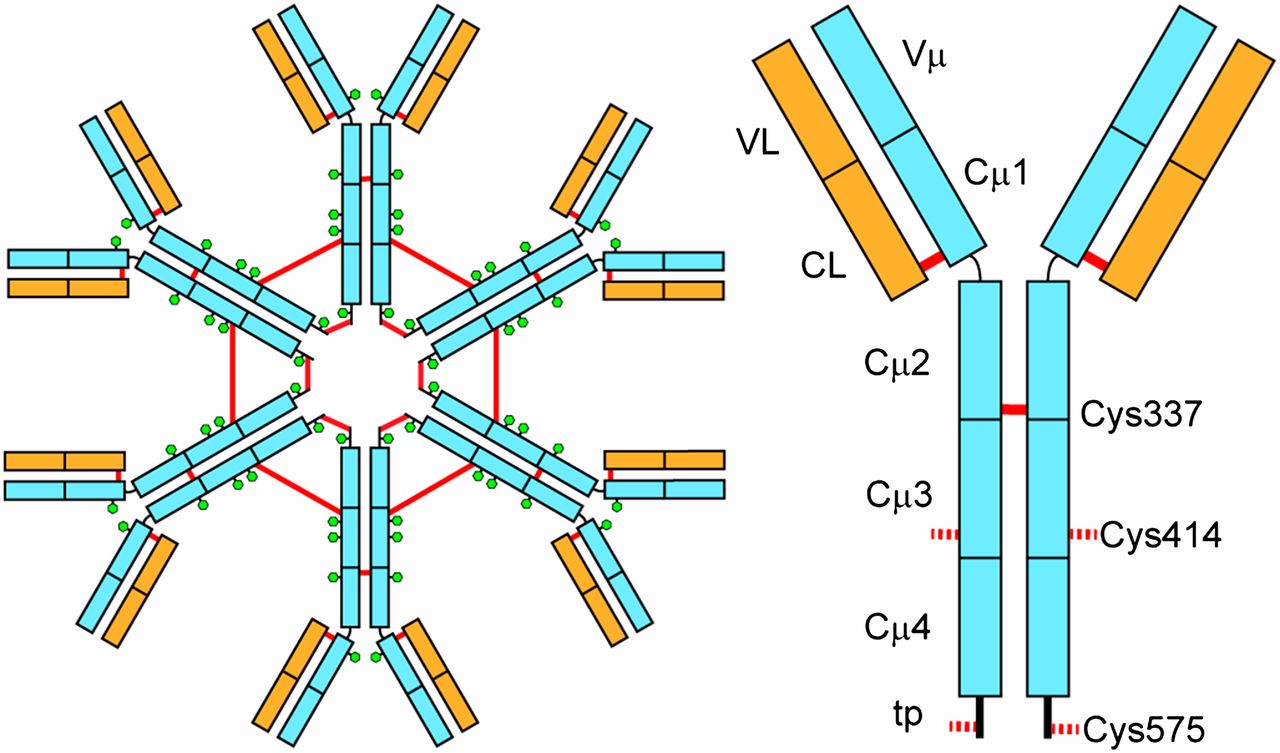
Auto immunity: Introduction and Mechanism
Introduction A condition resulted by the action of antibodies or immunologically competent cells. Cause structural or functional damage of the normal components of the body. Literally means ‘protection against self’ but means ‘injury to self’ in actual. Ehrlich postulated the concept of horror auto-toxicus. Was proposed while observing goats producing antibodies against erythrocytes from other … Read more