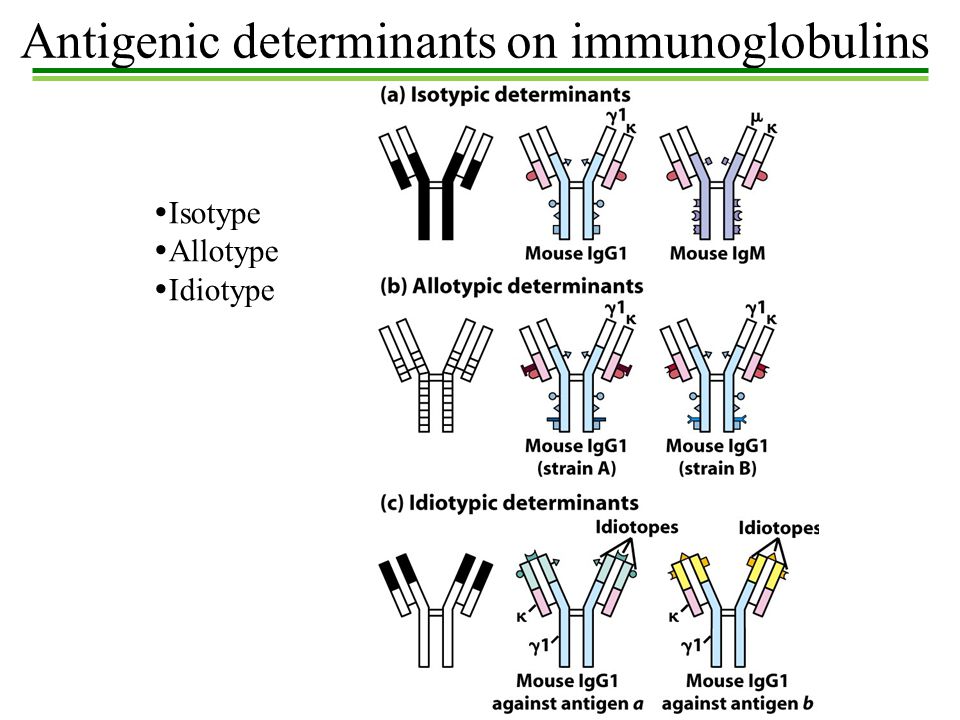
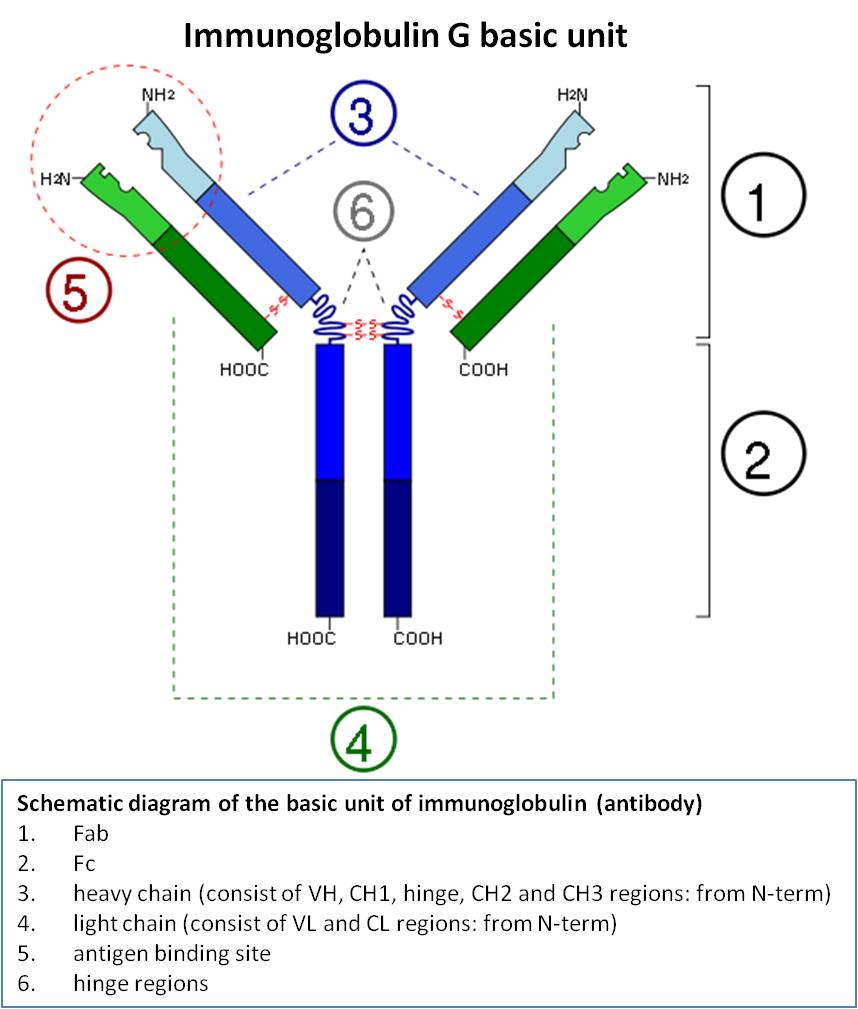
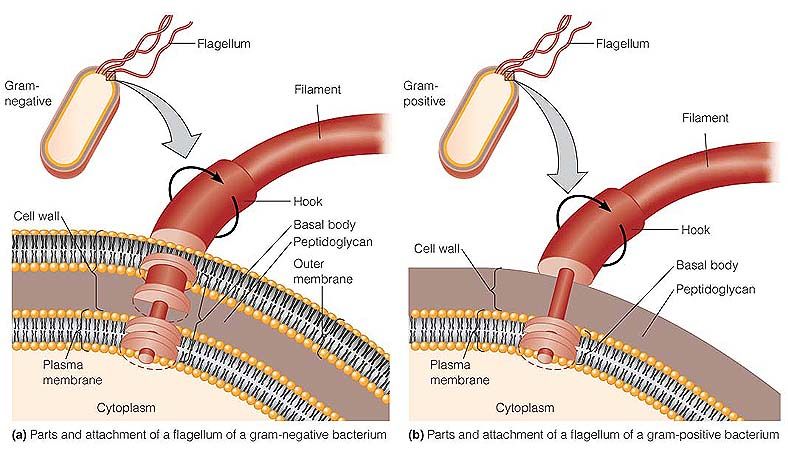
ELISA and its type
It is the abbreviated form of Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or EIA. It is similar in principle to Radio immune assay (RIA) but instead of radioactive substance it uses an enzyme. Chromogenic substrate is generated by reacting an enzyme conjugated with the antibody and a colorless substrate. Chromogenic substrate is a colored reaction product. Various enzymes … Read more